
Liabilities and equity make up the right side of the balance sheet and cover the financial side of the company. With liabilities, this is obvious—you owe loans to a bank, or repayment of bonds to holders of debt. Liabilities are listed at the top of the balance sheet because, in case of bankruptcy, they are paid back first before any other funds are given out. A balance sheet is one of the primary statements used to determine the net worth of a company and get a quick overview of its financial health. The ability to read and understand a balance sheet is a crucial skill for anyone involved in business, but it’s one that many people lack. In a restaurant, for example, there are many fixed assets necessary to run an effective business.

What is fixed asset accounting?
Many organizations implement a policy for tangible asset expenditures which sets a materiality threshold over which purchases will be capitalized. This can be for a single asset purchase or a group of similar fixed asset accounting assets purchased around the same time. Capitalizing relatively insignificant purchases does not improve the readability of financial statements and may end up costing an entity more than the asset’s value.
Capital Investment and Fixed Assets
Fixed asset accounting refers to the action of recording an entity’s financial transactions for its capital assets. For organizations reporting under US GAAP, ASC 360 is the appropriate accounting standard to follow. For most organizations, fixed assets are a significant investment and must be accounted for properly. As per IAS 16.30, a business entity can record the value of fixed assets in the balance sheet at the initial cost less any impairment and accumulated depreciation realized so far.
- If a business creates a company parking lot, the parking lot is a fixed asset.
- To determine how much of the net assets the client owns, consider an alternative formula that eliminates the fixed asset liabilities, which are the debts and financial obligations the company owes on those assets.
- Fixed assets are physical (or “tangible”) assets that last at least a year or longer.
- These items also appear in the cash flow statements of the business when they make the initial purchase and when they sell or depreciate the asset.
- Depreciation begins one month after a fixed asset is placed into service and continues until an item is fully depreciated or disposed of either through salvage or sale.
- In both cases, the external party wants to assess the financial health of a company, the creditworthiness of the business, and whether the company will be able to repay its short-term debts.
Carrying Amount Of The Fixed Assets
The revaluation method signifies that the fair value of the fixed asset will be calculated every time. The value less any depreciation and impairment will be recorded in the balance sheet of the business entity. The revaluation method is allowed only if fair value can be calculated with certainty.
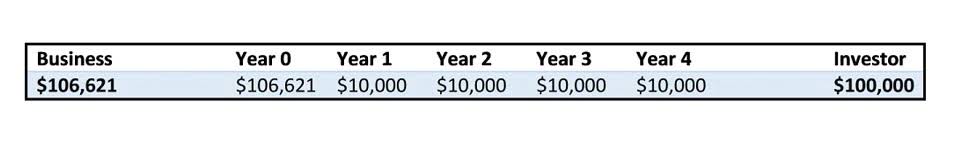
Capital investment is money invested in a company with the goal of advancing its commercial objectives. In this example, we can say that the service given by the weighing machine in its first year of life was $200 ($1,000 – $800) to the company. Therefore, after a certain period, the value of the exhausted asset will be zero. Due to the continuous extraction of minerals or oil, a point comes when the mine or well is completely exhausted—nothing is left.
The company then will depreciate these assets over the five-year period to account for their cost. The depreciation expense is moved to the income statement where it’s deducted from operating profit. Depending on what the asset is used for, this expense may be shown in cost of goods sold or in the selling, general and administrative category. On the other hand, current assets are assets that the company plans to use within a year and can be converted to cash easily. While current assets help provide a sense of a company’s short-term liquidity, long-term fixed assets do not, due to their intended longer lifespan and the inability to convert them to cash quickly. Net fixed assets are a crucial indicator of a company’s long-term asset value, reflecting the current worth of essential assets after depreciation and improvements.
This term is often used in financial statements to describe the value of a company’s long-term physical assets after accounting for accumulated depreciation, reflecting their current worth. The fixed assets include tangible assets, mostly as plants & machinery, buildings, equipment, furniture, etc. Accumulated depreciation is the total amount of depreciation expense that has been charged to profit and loss account from the date of purchase of the fixed asset.
- This asset section is broken into current assets and non-current assets, and each of these categories is broken into more specific accounts.
- Many organizations would not exist or generate revenue without their property, plant, and equipment.
- Assets are typically listed as individual line items and then as total assets in a balance sheet.
- On the other hand, private companies do not need to appeal to shareholders.
- This balance sheet compares the financial position of the company as of September 2020 to the financial position of the company from the year prior.
- Adding total liabilities to shareholders’ equity should give you the same sum as your assets.